 Studies
conducted among consumers in Finland, the UK, Spain and France have revealed clear
consumer demand for mobile TV services as well as important pointers regarding future
business models. Interim results from the pilot of DVB-H (Digital Video Broadcasting
for Handhelds) in Oxford, UK, conducted from October 2005 to March 2006, revealed
that 83% of participants were satisfied with the service and over three quarters
(76%) said they would take up the service within 12 months. In France, 68% said
they would pay for mobile TV services while over half (55%) in Spain were willing
to do so.
Studies
conducted among consumers in Finland, the UK, Spain and France have revealed clear
consumer demand for mobile TV services as well as important pointers regarding future
business models. Interim results from the pilot of DVB-H (Digital Video Broadcasting
for Handhelds) in Oxford, UK, conducted from October 2005 to March 2006, revealed
that 83% of participants were satisfied with the service and over three quarters
(76%) said they would take up the service within 12 months. In France, 68% said
they would pay for mobile TV services while over half (55%) in Spain were willing
to do so.
This article – which is extracted from a paper by Cosimo Palanga at CEFRIEL – considers
a scenario for the introduction of DVB-H. A STEM techno-economic model is developed,
evaluating the selection of the geographical areas and customer segments to be served,
the services to be provided, and the technology to be used to provide the services.
The main issue addressed is what type of value chain delivers the highest Net Present
Value (NPV) over a period of ten years.
Value chain
The main characteristic of the model is the analysis of the value chain. Three potential
actors are identified – the Service Provider, the Network Provider and the Content
Provider – and the scenarios listed below are considered.
- No actor is present.
- Only one actor is present.
- Service-Network Provider, where the service is provided and the network owned by
a single entity, which buys the contents from the Content Provider.
- Service-Content Provider, where the service is provided and the content is produced
and aggregated by a single entity, which rents the network from the Network Provider.
- Network-Content Provider, where the network is owned and the content produced and
aggregated by a single entity, which leases the network and sells the content to
the Service Provider.
- All, where all three actors are present.
The choice of scenario to evaluate is driven by a flag in the service User Data.
Business model structure
The overall structure of the model is shown below and the main elements are described
in the following section.
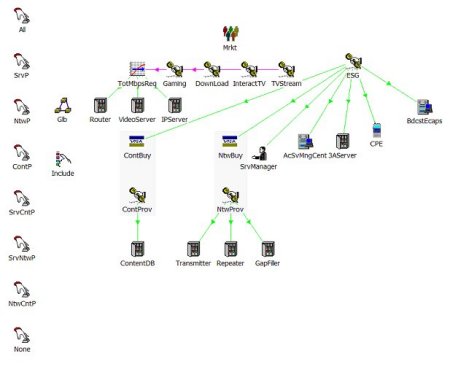
Business model structure (Source: CEFRIEL)
This view shows the market segment (Mrkt), the services offered (for the Service
Provider: ESG, TVStream, InteractTV, DownLoad, Gaming; for the Network Provider:
NtwProv; for the Content Provider: ContProv), and the resources (for the services:
BdcstEcaps, CPE, 3AServer, AcSvMngCent, SrvManager, IPServer, VideoServer and Router;
for the network: GapFiller, Repeater and Transmitter; for the content: ContentDB
and FilmProd). The transformation icon (TotMbpsReq) calculates the Mbit/s required
by type of locations. The variant icons (All, SrvP, NtwP, ContP, SrvCntP, SrvNtwP,
NtwCntP, None) represent the scenarios, construed as all the possible combinations
of the actors in the value chain. In the following sections, each element is described
in more detail.
Market
The market segment of the business model is based on the Italian population, with
the assumptions listed below.
- Covered proportion of population and the covered proportion of territory have a
linear relationship. As a result, the coverage factor converts a potential subscriber
into a reachable subscriber, and drives the number of base stations required to
provide coverage for those subscribers.
- The run period utilized is ten years, to reach 100% of Italian population coverage
in the final year.
- The age range of the subscribers is 18–65.
- The reachable subscribers generate demand for a service proportionally to the level
of penetration of that service.
- Traffic demands of broadband subscribers are expected to grow steadily throughout
the study period.
Services
The breakdown of services modelled by actor type is shown below:
|
Service Provider
|
ESG (electronic service guide) |
| TVStream (streaming TV) |
| InteractTV (interactive TV) |
| Download (on-demand video services and content synchronization) |
| Gaming (real-time gaming, assuming WiMAX technology as return channel) |
|
Network Provider
|
NtwProv (the base set of services required to keep a network running)
|
|
Content Provider
|
ContProv (the provision of content)
|
Cost elements
The functional requirements for each service are shown below:
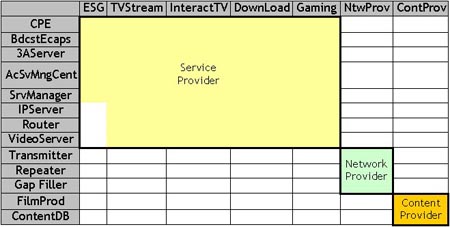
Service requirements (Source: CEFRIEL)
The individual resources are listed below, divided into two groups: those related
to the ESG (and used also for the other services), and those related to the remaining
services.
Service resources related to the ESG
|
CPE (Customer Premises Equipment)
|
The device used to connect to the DVB-H network; it can be a mobile phone or a PDA
or another device with an DVB-H receiver.
|
|
BdcstEcaps (Broadcast Encapsulator)
|
The gateway that enables broadcast delivery of IP content over DVB-H. These IP encapsulators
also perform the encryption of paid services.
|
|
3AServer (Access Authentication Authorization Server)
|
A server that provides authentication, authorization and accounting services for
applications such as network access or IP mobility. It is intended to work in both
local and roaming situations.
|
|
AcSvMngCent (Account and Service Management Centre)
|
An online service fulfillment and charging facility for paid mobile broadcast services.
A consumer who selects a pay service from the ESG is prompted to try it and buy
premium content. The Account and Service Management Centre produces the associated
billing data. The Account and Service Management Centre supports both postpaid and
prepaid subscriber types, in a single installation.
|
|
SrvManager (Service Manager)
|
The Service Manager is able to manage a large number of DVB-H subscribers to control
the broadcast and end-to-end protection of streams.
|
Service resources related to the remaining services
IPServer
|
A server responsible for accepting HTTP requests from clients and serving them Web
pages, which are usually HTML documents and linked objects (images, games scenarios,
etc.)
|
|
Router
|
A computer networking device that forwards data packets across an internetwork toward
their destinations.
|
|
VideoServer
|
A storage system that provides audio and video storage for a network of clients.
|
Cellular network and other assumptions
The model also includes cell equipment, comprising base station primary equipment,
one transmitter, two repeaters per transmitter, and five gap fillers per repeater,
and a base station link to the backbone network. The network resource planning has
been evaluated for each district within Italy to optimize the coverage.
Other resources include the ContentDB (content database) and the FilmProd, which
includes all elements required for the production of programming, from the first
cut to the storage and distribution of the programs.
Other assumptions have been made concerning:
- deployment speed
- height, effective radiated power, and coverage radius of SFN cell components (transmitter,
repeater, and gap filler)
- location of transmitter sites relative to population
- lag before sites work at full capacity
- connection, rental, and usage tariffs
- capital, maintenance, connection and rental costs.
Results and conclusions
The CEFRIEL paper states that the most accurate evaluation of each scenario can
be made using the NPV calculation. A discount rate of 10% is assumed. The graph
below shows the NPV of the investment for the scenarios Content Provider, NtwP,
ServiceProvider, and All.
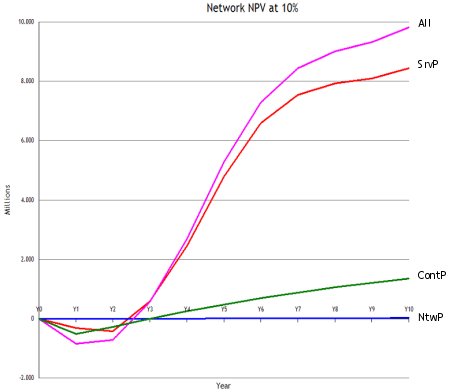
Network NPV at 10% (Source: CEFRIEL)
A positive NPV can be observed for all three scenarios from Y3. However, the highest
NPV is achieved under the All scenario. The CEFRIEL paper concludes that the All
variant seems to be the most suitable to provide broadcasting services to mobile
users, although the other variants also provide good results. This can be explained
by cost savings associated with vertical integration and high demand for broadcasting
services from mobile users.
The Center of Excellence For Research, Innovation, Education and Industrial Labs
(CEFRIEL) partnership in Milan was established
in 1988 as a partnership between organisations from academia, ICT business and public
administration. CEFRIEL is one of the main centres for technology transfer in the
ICT field, and a leading Italian player in ICT research, innovation and education.